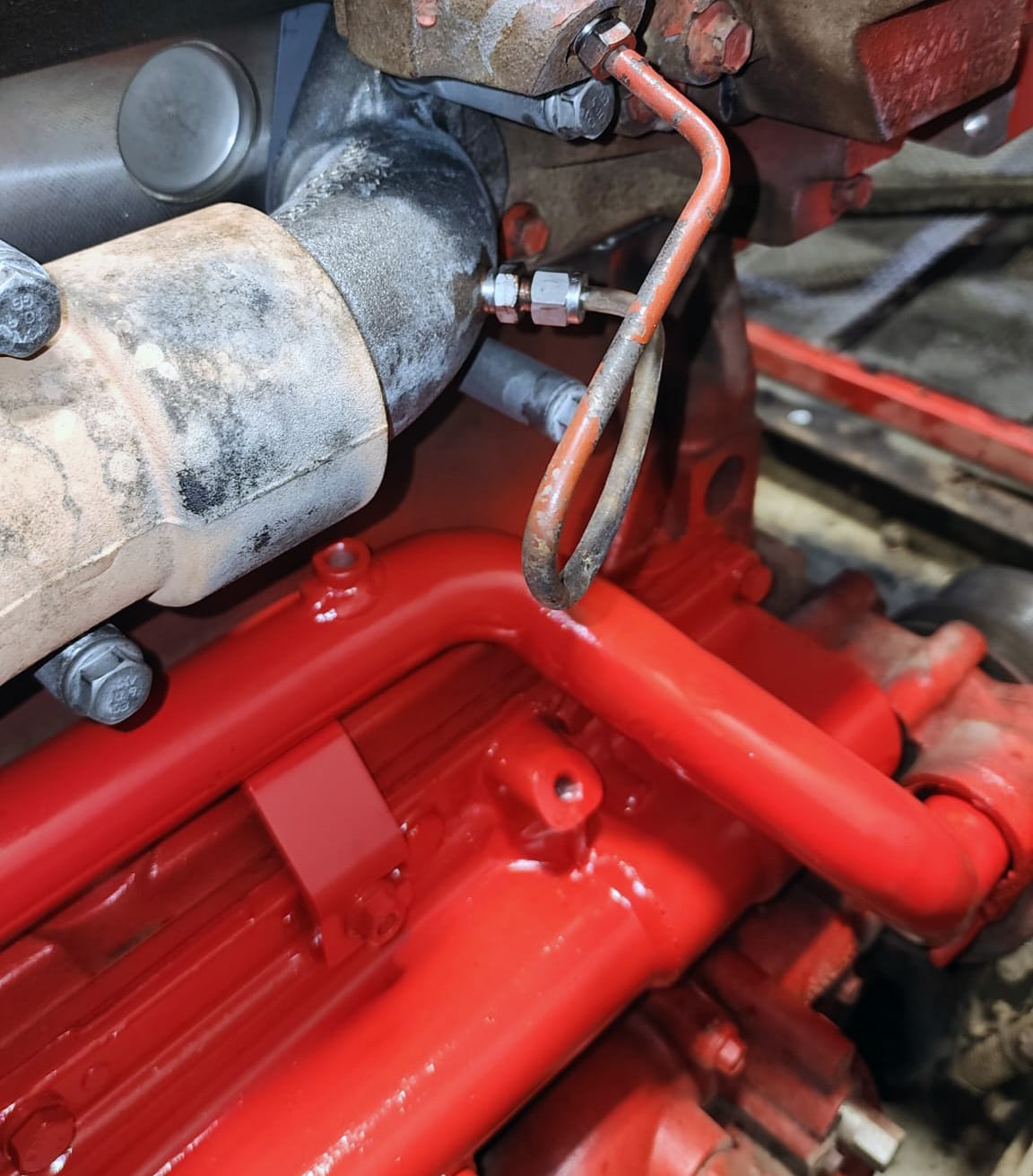
What Does EGR Do in a Diesel Engine?
The EGR system is designed to reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by recirculating a portion of exhaust gases back into the intake. This lowers combustion temperatures and helps the engine meet emissions regulations. Key components of the EGR system include the EGR cooler, EGR valve, and associated plumbing, all working together to reduce pollution and keep the engine compliant with environmental laws.
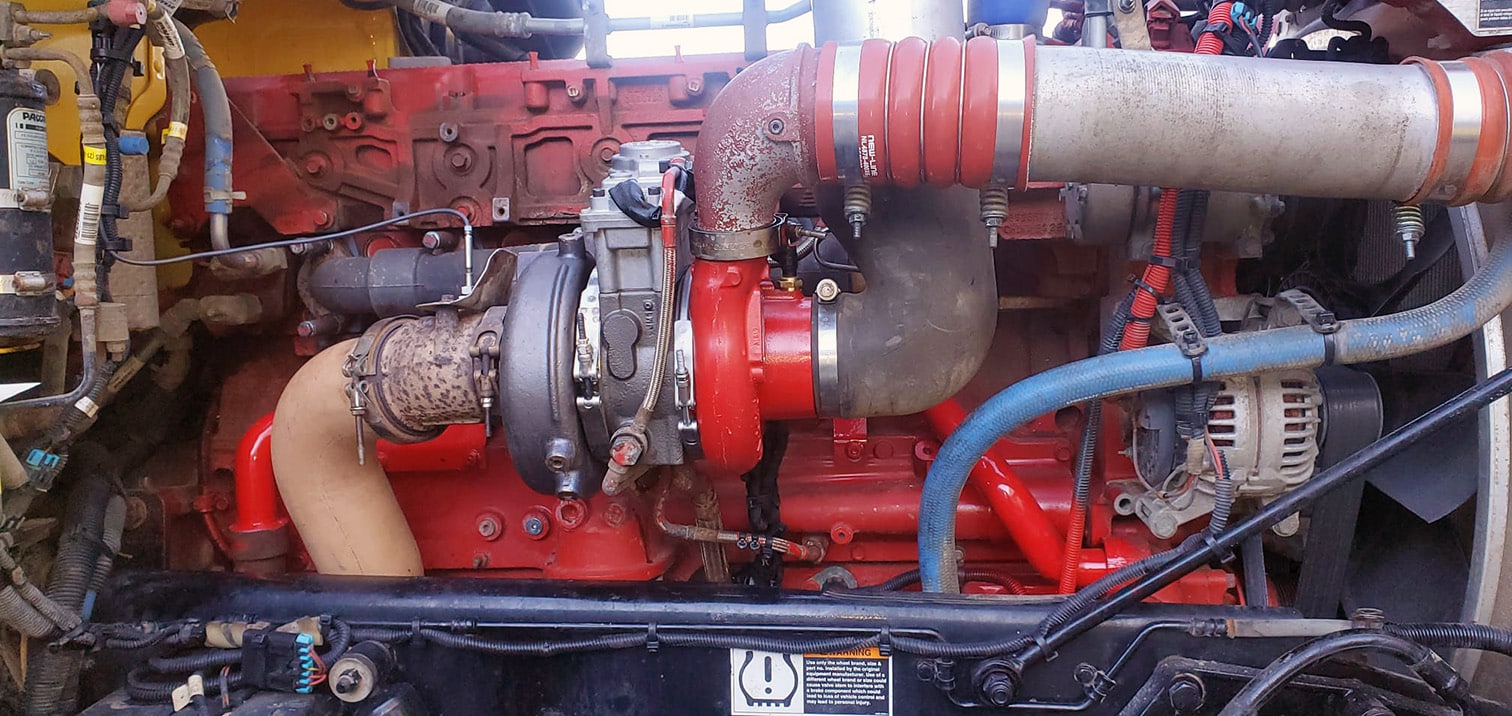
Benefits of EGR in a Diesel Engine
- Lower NOx Emissions – EGR significantly reduces NOx emissions, helping engines meet strict environmental standards.
- Improved Engine Longevity – Properly maintained EGR systems can prevent excessive cylinder temperatures and reduce wear on internal components.
- Fuel Efficiency Under Load – Modern EGR tuning optimizes fuel economy when operating within emissions-compliant conditions.
What Happens When the EGR System is Removed?
While some trucks come with EGR already removed, others undergo an EGR delete aftermarket. If an EGR system is deleted, several engine parameters must be recalibrated to ensure reliable performance. Here are the key adjustments that must be made:
1. Fueling Adjustments
The EGR system changes the way fuel is delivered to the engine. Without EGR, the engine will require recalibrated fueling to maintain efficiency and power output without excessive smoke or high exhaust gas temperatures (EGTs). Proper fueling adjustments ensure the Cummins ISX or X15 engine runs smoothly without unnecessary strain.
2. Injection Timing Adjustments
Engines with EGR are designed to inject fuel at specific points in the combustion cycle to optimize emissions and efficiency. When the EGR is deleted, the engine’s injection timing must be adjusted to compensate for the reduced exhaust gas recirculation.
3. Turbo Mapping and Boost Control
The turbocharger is mapped to work with EGR flow, affecting spool-up times, boost pressure, and exhaust backpressure. If the EGR is deleted, turbo mapping may need to be adjusted to optimize performance and prevent issues such as turbo lag or excessive backpressure. A properly configured turbo ensures the best efficiency and power for trucks like Kenworth and Peterbilt models with a Cummins ISX or X15 engine.
4. Cooling System Considerations
In many cases, the EGR cooler remains in place to allow coolant to continue circulating. However, if the EGR cooler is removed or bypassed, a coolant transfer tube, such as our in-house manufactured EGR bypass tube (part numbers 4367122 and 5575183), is required to maintain proper coolant flow and prevent overheating. This is especially important for long-haul trucks like Freightliner and International models equipped with the Cummins ISX and X15.
Why You Might Encounter a Truck with EGR Already Deleted
When purchasing a used commercial truck, it’s not uncommon to find that the previous owner has already removed the EGR system. This is especially true for trucks that have been repurposed for off-highway use or used in regions with different emissions requirements. If you buy a truck with an EGR delete, ensure the proper modifications have been made to fueling, timing, and turbo controls to prevent long-term reliability issues.
Final Thoughts
EGR deletes on Cummins ISX and X15 engines are a common modification, but they come with necessary recalibrations to ensure the engine runs efficiently and reliably. If you own or are considering purchasing a truck with an EGR delete, be aware of the necessary changes required to keep the engine in top condition. If the EGR cooler has been removed, a proper EGR bypass tube should be installed to maintain cooling system integrity.
For more information on EGR bypass tubes, turbochargers, and performance solutions for your Cummins ISX or X15, contact us at Vara Turbo Technics. We offer expert advice and top-quality components to keep your engine running at peak performance.


